Brought to you by the world’s leading transplant clinicians, Textbook of Organ Transplantation provides a complete and comprehensive overview of modern transplantation in all its complexity, from basic science to gold-standard surgical techniques to post-operative care, and from likely outcomes to considerations for transplant program administration, bioethics and health policy.
Beautifully produced in full color throughout, and with over 600 high-quality illustrations, it successfully
- Provides a solid overview of what transplant clinicians/surgeons do, and with topics presented in an order that a clinician will encounter them.
- Presents a holistic look at transplantation, foregrounding the interrelationships between transplant team members and non-surgical clinicians in the subspecialties relevant to pre- and post-operative patient care, such as gastroenterology, nephrology, and cardiology.
- Offers a focused look at pediatric transplantation, and identifies the ways in which it significantly differs from transplantation in adults.
- Includes coverage of essential non-clinical topics such as transplant program management and administration; research design and data collection; transplant policy and bioethical issues.
Editors are Allan D. Kirk, Stuart J. Knechtle, Christian P. Larsen, Joren C. Madsen, Thomas C. Pearson, and Steven A. Webber.
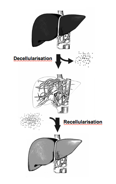
I.M. Sauer, N. Raschzok und P. Neuhaus contributed chapter 47: „
Artificial Liver, In Vivo Tissue Engineering, and Organ Printing – Solutions for Organ Scarcity“
The Wiley-Blackwell book (ISBN: 978-1-118-87014-3, 1880 pages) is available
here.