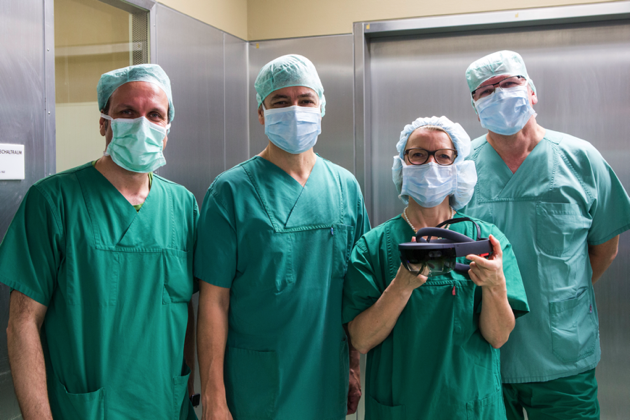
Comparison of AR HMDs in Visceral Surgery

Recent developments in the field of augmented reality (AR) have enabled new use cases in surgery. Initial set-up of an appropriate infrastructure for maintaining an AR surgical workflow requires investment in appropriate hardware. We compared the usability of the Microsoft HoloLens and Meta 2 head mounted displays (HMDs). Fifteen medicine students tested each device and were questioned with a variant of the System Usability Scale (SUS). Two surgeons independently tested the devices in an intraoperative setting.
In our adapted SUS, ergonomics, ease of use and visual clarity of the display did not differ significantly between HMD groups. The field of view (FOV) was smaller in the Microsoft HoloLens than the Meta 2 and significantly more study subjects (80% vs. 13.3%; p < 0.001) felt limited through the FOV. Intraoperatively, decreased mobility due to the necessity of an AC adapter and additional computing device for the Meta 2 proved to be limiting. Object stability was rated superior in the Microsoft HoloLens than the Meta 2 by our surgeons and lead to increased use.
We examined the Meta 2 and the Microsoft HoloLens and found key advantages in the Microsoft HoloLens which provided palpable benefits in a surgical setting.