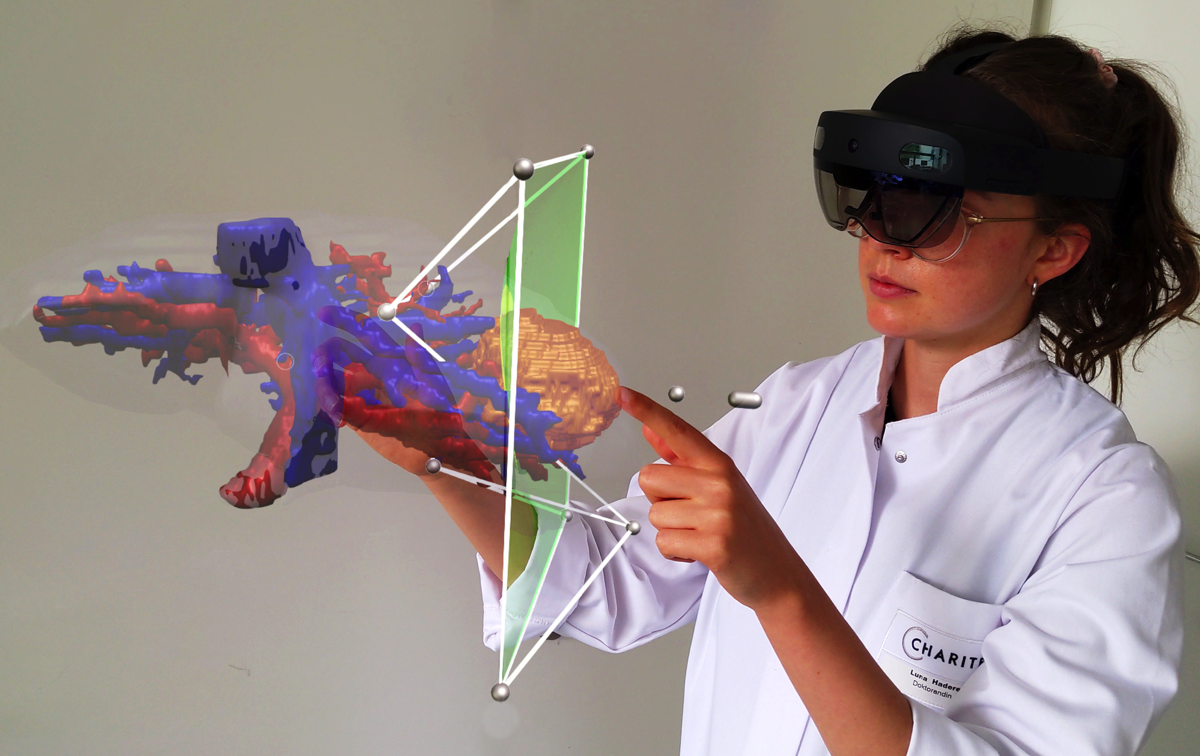
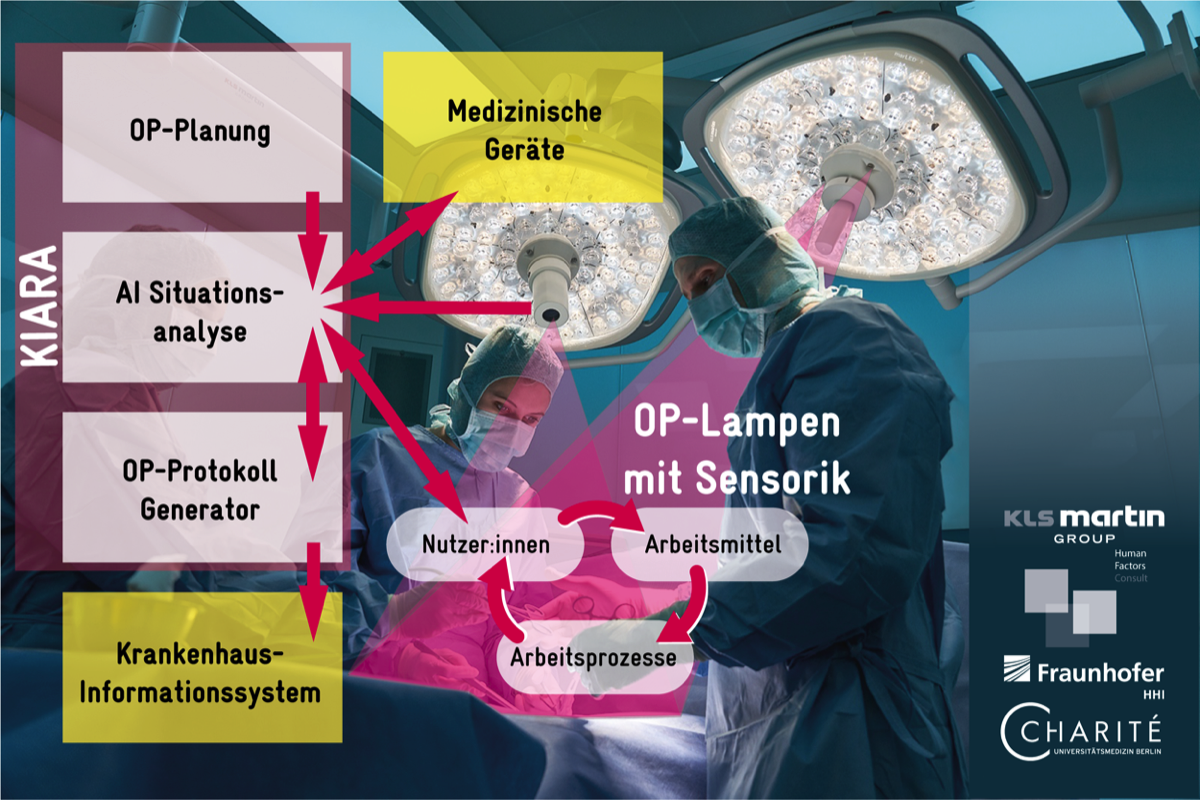
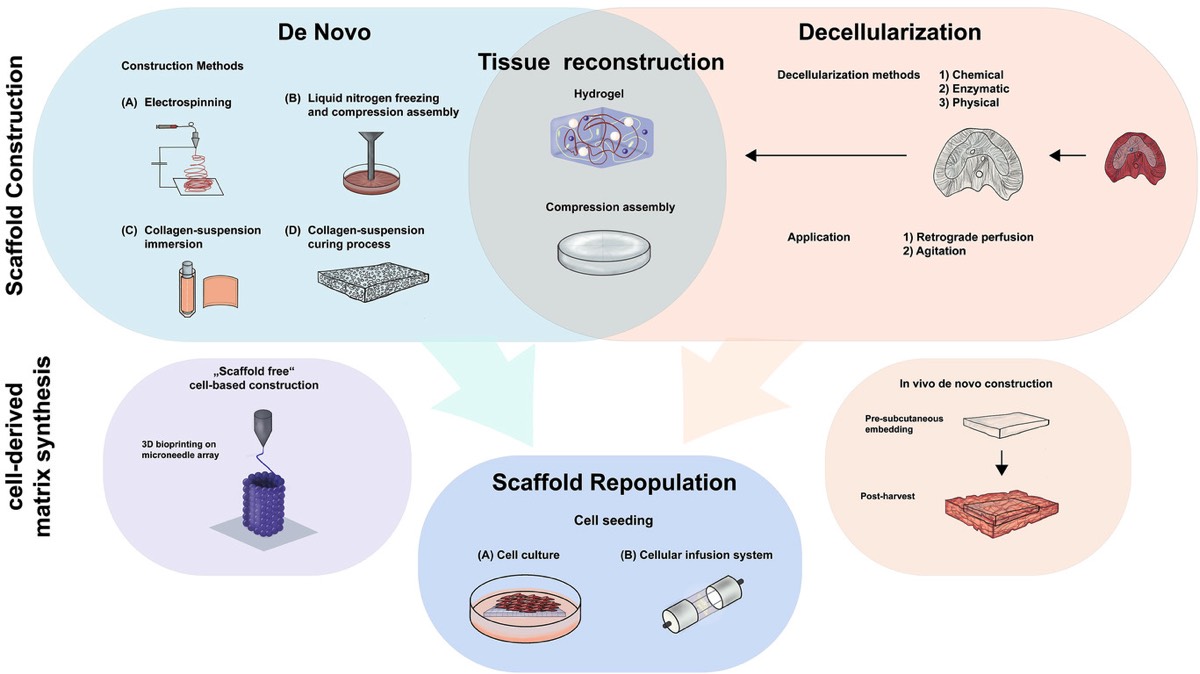
Priv,-Doz. Dr. med. Felix Krenzien and
Dr. Jennifer Kirwan (Technologieplattform Metabolomik, Max-Delbrück-Centrum für Molekulare Medizin, Berlin) successfully applied for a grant within the
Else Kröner Fresenius Stiftung funding line: Translational Research.
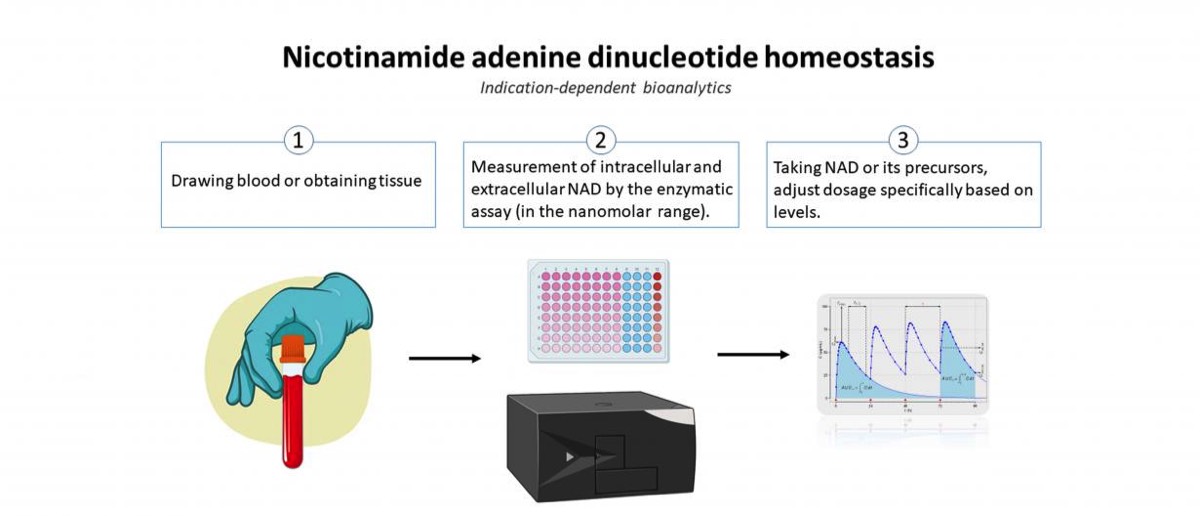
Recently, the molecule nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) has attracted attention as it is involved in various important regulatory mechanisms, immune signaling, aging and regenerative processes. In this regard, it occupies key positions in many redox reactions of the body due to its role as a redox couple (NAD as an oxidized species and NADH as a reduced species). Consequently, NAD homeostasis (the maintenance of NAD in cells) is considered essential. The scientific consensus for many years was that the oxidized species resides exclusively in the intracellular milieu (iNAD). However, recent findings indicate that NAD also exists extracellularly (eNAD) and it is present in virtually all body fluids (from lymph to saliva to blood plasma). Based on these findings, precursors of NAD have recently been approved by the FDA and are commercially available. Measurement of eNAD in blood plasma is problematic due to its low concentration in the nanomolar range. However, quantifying eNAD plasma levels but also eNAD concentrations in cells is necessary to monitor the intake of NAD or its precursors and to adjust their dosage precisely.
The primary objective of this project is to validate, bioanalyze,and to document the assay for eNAD according to the ICH-M10 guidance document endorsed by the U. S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Adherence to the principles presented in this guideline should improve the quality and consistency of bioanalytical data, thereby supporting assay development and market approval. In addition, the assay will also be established for the measurement of intracellular NAD (iNAD), and validation of iNAD quantification will also be performed according to the guideline.
In the second part of the project, a clinical study will be conducted to determine whether the intake of nicotinamide riboside (precursor of NAD) leads to a change in eNAD and iNAD. Thus, the basis for an indication-dependent bioanalysis of the measurement of NAD will be developed to monitor the intake of NAD and its precursor or to adjust the dosage specifically on the basis of the quantification.